General Information about Gynecological Cancer
Gynecological cancers encompass cancers of the female reproductive system which includes the cervix, vulva, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and vagina. Substantial improvements have been made in the detection and treatment of gynecological cancers in the last 2 decades.
Facts about Gynecological Cancer
- Cervical cancer - Second most common cancer in women. HPV (human papilloma virus) is the greatest risk factor associated with cervical cancer. It is also associated with smoking. Early detection of cervical cancer includes Pap smear screening. Recently the FDA has approved vaccinations for HPV, which may decrease the incidence of cervical cancer.
- Vulvar cancer - The least common of all gynecological cancers, accounting for less than 5% of all gynecological cancers. Disease typically affects elderly women. HPV has shown a correlation with incidence of vulvar cancer.
- Endometrial (or Uterine) cancer - Includes several types of malignancies that originate from the inner lining of the uterus, which is also known as the endometrium. Endometrial cancer is the most common cancer appearing in the female genital tract in the United States. Some common risk factors include high estrogen levels, obesity, hypertension, endometrial hyperplasia, and hypertension.
- Ovarian cancer - Disease has shown a correlation with increased incidence in more industrialized nations. The risks of developing ovarian cancer also increases with age and decreases with the numbers of pregnancy.
Signs and Symptoms of Gynecological Cancer
- Cervical cancer - Second most common cancer in women. HPV (human papilloma virus) is the greatest risk factor associated with cervical cancer. It is also associated with smoking. Early detection of cervical cancer includes Pap smear screening. Recently the FDA has approved vaccinations for HPV, which may decrease the incidence of cervical cancer.
- Vulvar cancer - The least common of all gynecological cancers, accounting for less than 5% of all gynecological cancers. Disease typically affects elderly women. HPV has shown a correlation with incidence of vulvar cancer.
- Endometrial (or Uterine) cancer - Includes several types of malignancies that originate from the inner lining of the uterus, which is also known as the endometrium. Endometrial cancer is the most common cancer appearing in the female genital tract in the United States. Some common risk factors include high estrogen levels, obesity, hypertension, endometrial hyperplasia, and hypertension.
- Ovarian cancer - Disease has shown a correlation with increased incidence in more industrialized nations. The risks of developing ovarian cancer also increases with age and decreases with the numbers of pregnancy.
Anatomy of Gynecological Cancer
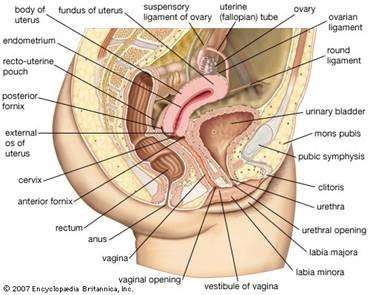
Helpful Terms Regarding Gynecological Cancer
- Dysuria - Pain with urination which can be a temporary side effect of radiation treatments.
- HDR (High Dose Rate) brachytherapy - A form of internal radiation where a radioactive source is temporarily implanted for gynecological cancer treatment.
- Linear Accelerator - The machine that delivers the radiation treatment.
- Lymph node dissection - Surgical removal of lymph nodes, in gynecological cancer the lymph nodes in the pelvis are dissected.
- TAH/BSO - Total abdominal hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oopherectomy - surgical procedure for uterine cancer.
Treatment of Gynecological Cancer
Cervical cancer
Treatment of early stages requires a hysterectomy (surgical removal of whole uterus/cervix and a portion of the vagina) and sampling of lymph nodes. A fertility sparing surgery known as a trachelectomy may also be performed in very early stage cervical cancers. This involves the removal of the cervix preserving the uterus and ovaries. Early stage disease may also be treated with external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and internal radiation (brachytherapy). Larger more advanced stages are usually treated with radiation therapy and chemotherapy.
Vulvar cancer
Surgery is the main treatment of choice and usually involves a radical vulvectomy (complete removal of the vulva). The use of chemotherapy and radiation therapy can be utilized in more advanced stages.
Endometrial (or Uterine) cancer
Primary treatment of early stage disease is surgery. Women with higher risk disease may need additional radiation therapy to improve their chance of cure. Chemotherapy may be necessary in patients with more advanced staged uterine cancer.
Ovarian cancer
Often treated with a combination of chemotherapy and surgery, but sometimes use of radiation therapy can improve outlook. Depending on the stage and grade of the tumor when diagnosed, surgery can include the removal of all or some gynecological organs. Partial surgeries can include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the uterus. A complete resection of all structures is known as the TAHBSO surgery (total abdominal hysterectomy and bi-lateral salpingo-oopherectomy).
Vaginal cancer
Treatment varies depending on your specific case. It often involves surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The optimal treatment is determined by your oncology team.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the side effects from radiation to the gynecological organs (pelvis)?
A: Radiation treatments are designed to be localized and site specific. For this reason, any potential side effects are directly related to the area being treated. Common acute side effects during radiation treatments to the pelvis include redness of the skin, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Long term side effects can vary depending on the area treated. Most side effects are mild and temporary.
Q: What diet should I be on during radiation treatments?
A: Patients that are at risk for diarrhea should minimize their fiber intake. If you do have loose stools or diarrhea we recommend eating plain oatmeal, white rice, ripe bananas, applesauce, white toast, canned fruit without the skins, such as peaches and pears, white pasta noodles, cream of rice cereal, and plain unsweetened graham crackers. If you are having diarrhea make sure you are properly hydrated with fluids.

